Services
Our Heat-Treatment Services
We provide a complete range of advanced heat-treatment solutions designed to improve the strength, durability, and performance of metal components. With precision-controlled processes, skilled technicians, and modern equipment, we ensure consistent quality, reliable results, and industry-standard perfection for every project.
Annealing is a controlled heat treatment process used to soften metals, relieve internal stresses, and improve ductility, machinability, and overall structural stability. In this process, the material is heated to a specific temperature, held for a defined period, and then slowly cooled under controlled conditions to refine the grain structure and reduce hardness. Annealing enhances uniformity, minimizes distortion, and improves dimensional accuracy, making components easier to machine, form, and process further. It is widely applied to steels and alloys to restore material properties after cold working, forging, or machining and to prepare components for subsequent heat treatment operations.

Atmosphere heat treating is a controlled heat treatment process in which metal components are heated in a precisely regulated furnace atmosphere to prevent oxidation and achieve consistent metallurgical results. By controlling gases such as carbon-rich or neutral atmospheres, this process improves surface quality, hardness, strength, and wear resistance while maintaining dimensional accuracy. Atmosphere heat treating is commonly used for processes such as annealing, carburizing, carbonitriding, normalizing, and hardening, ensuring uniform case depth, repeatable properties, and reliable performance for critical industrial components.
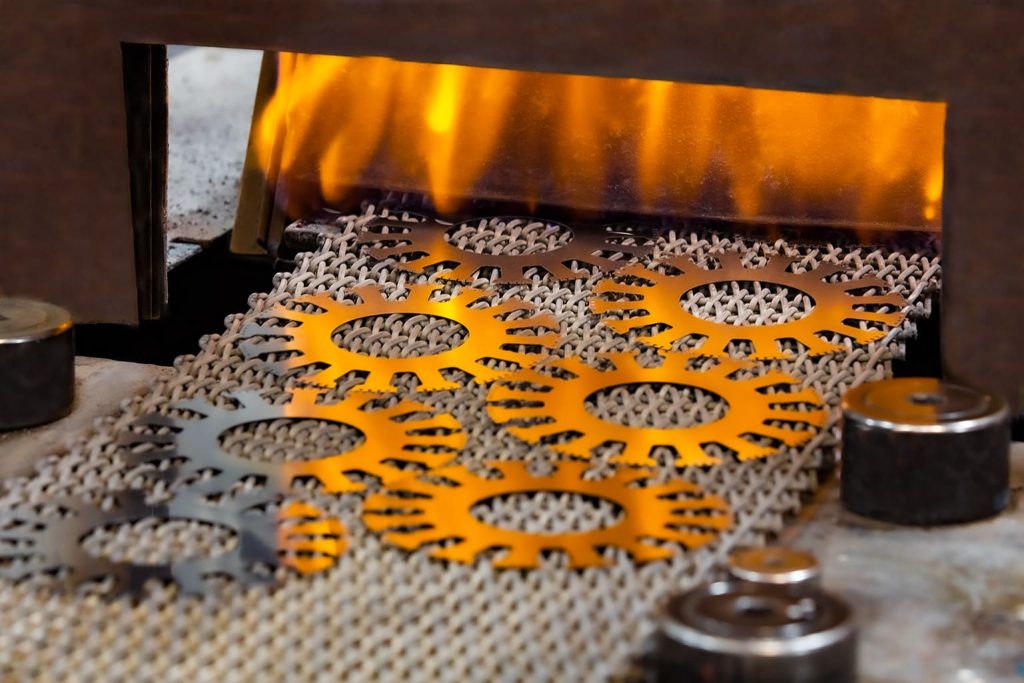

Atmosphere processes involve heat treating metal components in furnaces with carefully controlled gaseous environments to achieve precise mechanical and metallurgical properties. By regulating the furnace atmosphere, these processes prevent surface oxidation and decarburization while enabling treatments such as annealing, carburizing, carbonitriding, carbon restoration, normalizing, and hardening. Atmosphere processes ensure uniform hardness, improved wear resistance, consistent case depth, and excellent dimensional stability, making them ideal for high-performance and critical engineering applications.
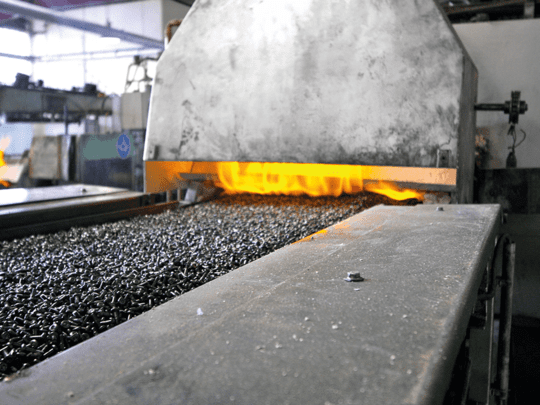

Carbon restoration is a specialized atmosphere heat treatment process used to replenish carbon content on the surface of steel components that has been lost during prior machining, forging, or heat treatment operations. By introducing a controlled carbon-rich atmosphere at elevated temperatures, this process restores proper surface chemistry, improves hardness response, and ensures uniform mechanical properties. Carbon restoration helps prevent soft surface layers, enhances wear resistance, and prepares components for subsequent heat treatment processes, ensuring consistent performance and reliability.
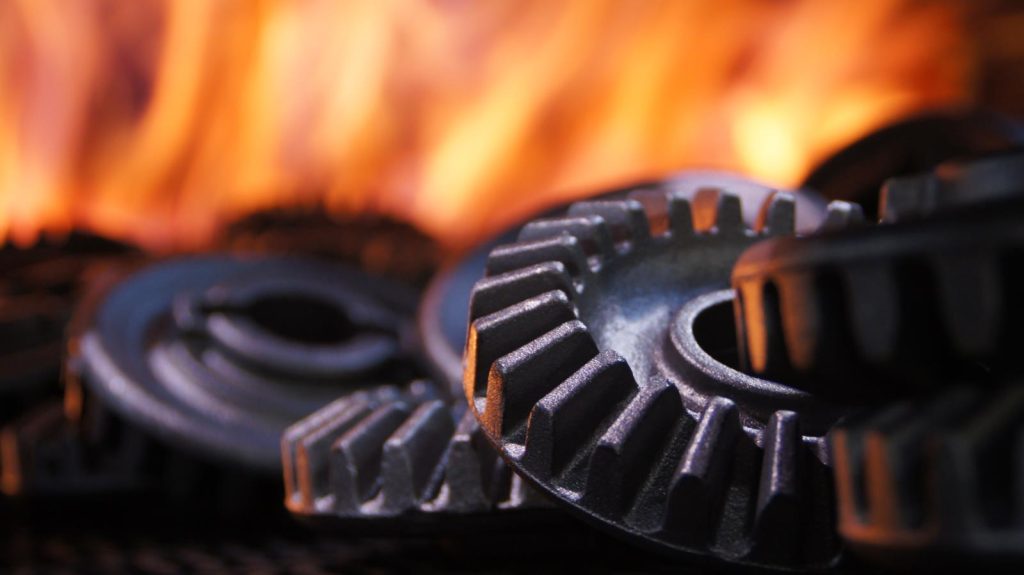

Carburizing is a thermochemical heat treatment process in which carbon is diffused into the surface of low-carbon steel at elevated temperatures to create a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a tough and ductile core. This controlled atmosphere process enhances surface hardness, fatigue strength, and resistance to wear and impact without compromising internal strength. Carburizing is widely used for components such as gears, shafts, bearings, and automotive parts where high surface durability and long service life are critical.

Carbonitriding is a controlled atmosphere heat treatment process in which both carbon and nitrogen are diffused into the surface of steel at elevated temperatures to produce a hard, wear-resistant case with improved fatigue strength. This process offers better hardness penetration and enhanced resistance to wear and deformation while maintaining a tough core. Carbonitriding is especially suitable for small to medium-sized components such as gears, fasteners, shafts, and automotive parts where high surface hardness, dimensional stability, and consistent performance are required.
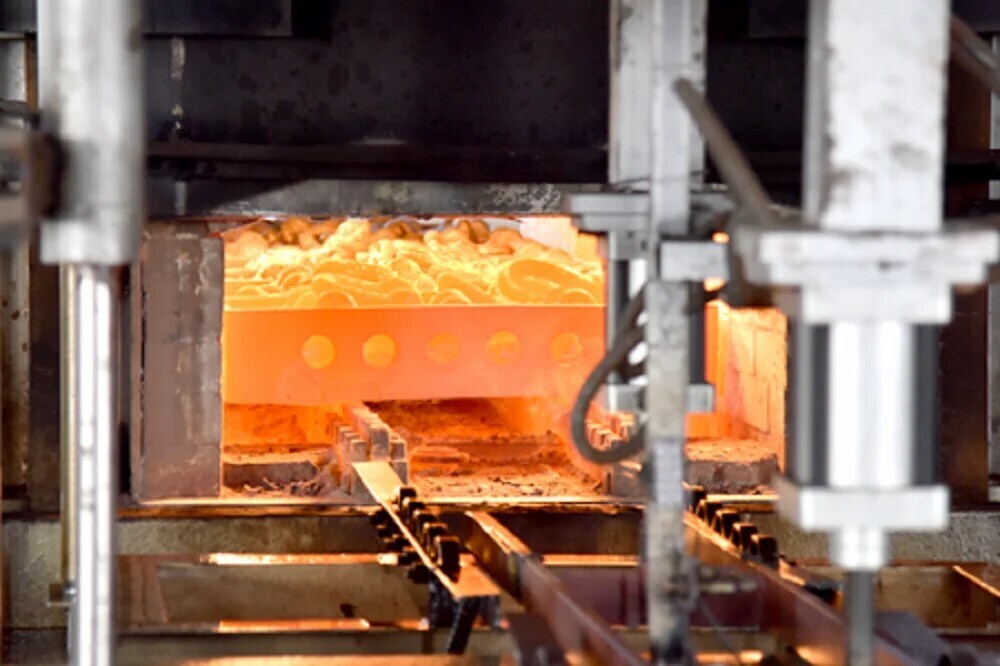

Case hardening is a heat treatment process that enhances the surface hardness of steel components while preserving a tough, ductile core. By modifying the surface layer through controlled thermochemical methods, this process improves wear resistance, fatigue strength, and load-bearing capacity without compromising internal toughness. Case hardening is widely used for components such as gears, shafts, pins, and automotive parts where a durable surface and long service life are essential.

Cryogenic (deep freezing) treatment is a specialized process in which metal components are cooled to extremely low temperatures to enhance material performance and dimensional stability. By transforming retained austenite into martensite and refining the microstructure, this process improves hardness, wear resistance, fatigue life, and overall durability. Cryogenic treatment is commonly used for tool steels, dies, gears, and precision components to extend service life, reduce residual stresses, and achieve consistent, long-term performance.

Fixture tempering is a controlled tempering process carried out using specially designed fixtures to hold components securely in position during heating and cooling. This method minimizes distortion, maintains dimensional accuracy, and ensures uniform stress relief after hardening or quenching. Fixture tempering is ideal for precision and thin-section components where tight tolerances, shape retention, and consistent mechanical properties are critical.
Hardening is a heat treatment process used to increase the hardness, strength, and wear resistance of steel components by heating them to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling through quenching. This process alters the metal’s microstructure to achieve high surface and core hardness, making components capable of withstanding heavy loads and abrasion. Hardening is widely applied to tools, gears, shafts, and engineering parts where durability and performance are essential.

Isothermal annealing is a controlled heat treatment process used to produce a uniform and refined microstructure in steel by holding the material at a constant temperature after austenitizing. This process reduces hardness variations, improves machinability, and enhances dimensional stability by allowing transformation to occur evenly throughout the material. Isothermal annealing is especially beneficial for alloy steels and components requiring consistent mechanical properties and reliable performance.

Aluminium heat treatment is a controlled process used to enhance the mechanical properties of aluminium alloys by precisely heating and cooling them to achieve the desired strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. Through processes such as solution treating and aging, this treatment improves structural stability and performance while maintaining lightweight characteristics. Aluminium heat treatment is widely applied in automotive, aerospace, and engineering components where high strength-to-weight ratio and durability are essential.

Masking is a protective process used during heat treatment to selectively shield specific areas of a component from exposure to heat or chemical diffusion. By applying specialized masking materials or compounds, this process prevents unwanted hardening or surface modification in critical zones. Masking ensures precise treatment results, maintains dimensional accuracy, and allows controlled performance characteristics in components with complex designs or functional requirements.

Neutral hardening is a heat treatment process in which steel components are heated and hardened in a controlled, neutral atmosphere that prevents oxidation, scaling, and decarburization. This process ensures uniform hardness throughout the component while maintaining clean surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Neutral hardening is ideal for parts that require consistent mechanical properties, high strength, and minimal surface contamination after heat treatment.

Nitriding is a thermochemical heat treatment process in which nitrogen is diffused into the surface of steel to create a hard, wear-resistant layer without the need for quenching. This low-distortion process improves surface hardness, fatigue strength, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability while maintaining core toughness. Nitriding is ideal for precision components such as gears, shafts, dies, and tooling where long service life and consistent performance are critical.

Normalizing is a heat treatment process used to refine grain structure, improve uniformity, and enhance the mechanical properties of steel. In this process, the material is heated to a specified temperature and then cooled in air, resulting in improved strength, toughness, and dimensional stability. Normalizing helps eliminate internal stresses and is commonly applied to components after forging, casting, or machining to prepare them for further processing or service.

Precision gas carburizing is an advanced atmosphere heat treatment process that accurately controls carbon diffusion into the surface of steel components to achieve precise case depth and uniform hardness. By using carefully regulated gas atmospheres and temperature control, this process delivers excellent wear resistance, fatigue strength, and consistent metallurgical properties while maintaining core toughness and dimensional accuracy. Precision gas carburizing is ideal for high-performance components such as gears, shafts, and automotive parts where tight tolerances and repeatable results are essential.

Quenching is a heat treatment process in which metal components are rapidly cooled after heating to a specified temperature to achieve increased hardness and strength. By using controlled cooling media such as oil, water, or polymer solutions, quenching transforms the metal’s microstructure to enhance wear resistance and load-bearing capacity. This process is critical for achieving desired mechanical properties and is commonly followed by tempering to improve toughness and reduce internal stresses.

Selective hardening is a specialized heat treatment process in which only specific areas of a component are hardened while the remaining sections retain their original toughness and ductility. By precisely controlling heat application and quenching, this process enhances wear resistance and strength in critical zones without affecting the overall structure. Selective hardening is ideal for components such as gears, shafts, cams, and tools where localized durability and performance are required.

Solution treating is a heat treatment process in which alloy components are heated to a specific temperature to dissolve soluble phases into a solid solution, followed by rapid cooling to retain a uniform microstructure. This process improves strength, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties while preparing the material for subsequent aging or precipitation hardening. Solution treating is commonly applied to aluminum alloys, stainless steels, and other high-performance materials requiring precise property control.

Spheroidize annealing is a specialized heat treatment process used to soften high-carbon and alloy steels by transforming cementite into a spheroidal form within the ferrite matrix. This process significantly improves machinability, ductility, and formability while reducing hardness and tool wear during machining. Spheroidize annealing is commonly applied to tool steels, bearing steels, and components that require extensive machining or cold forming before final hardening.

Steel hardening is a heat treatment process in which steel is heated to a precise temperature and then rapidly quenched to increase hardness, strength, and wear resistance. This controlled transformation of the steel’s microstructure enables components to withstand heavy loads, abrasion, and impact. Steel hardening is commonly followed by tempering to balance hardness with toughness, ensuring reliable performance and long service life in demanding applications.

Stress relieving is a heat treatment process used to reduce residual stresses that develop in metal components during machining, welding, forging, or heat treatment. By heating the material to a controlled temperature below its transformation range and cooling it gradually, this process minimizes distortion, improves dimensional stability, and enhances service performance. Stress relieving is essential for maintaining accuracy, preventing cracking, and ensuring long-term reliability of precision and heavy-duty components.
Straightening is a corrective process used to restore the dimensional accuracy and alignment of metal components that may have warped or distorted during manufacturing or heat treatment. By applying controlled mechanical force, often combined with thermal techniques, this process brings parts back within specified tolerances without compromising material properties. Straightening ensures proper fit, function, and reliability of components, especially in precision and critical engineering applications.
List Of Equipments
Atmosphere / Oil Quench Furnaces
2 Atmosphere Oil Quench Furnaces
Capacity: 1 Ton
Chamber Size: 900mm x 2250mm Length
Temperature Range: 750″c to 1000″c
Quenching Medium: Oil Quench
- Oil Quench Tank Capacity :
10Ft(H) X 9Ft(W) X 10Ft(L) – 16,000 Litres
Atmosphere Heat Treatment Processes
Atmosphere Hardening
Atmosphere Carbonitriding
Atmosphere Carbon Restoration
Atmosphere Carburizing
Atmosphere Normalizing
Atmosphere Annealing
Water Quench Facility
Capacity: Up to 1,500 Kgs
Tank Size: 10Ft(H) X 9Ft(W) X 10Ft(L)
Temper Furnaces
Capacity: Up to 1,500 Kgs
Chamber Size: 1000mm x 250mm Length
Max Temperature: Up to 750″c
Tempering & Stress Relief Processes
Age Hardening
Anneal for Machining
Full Annealing
Code Stress Relieving
Tempering
Stress Relieving
Additional Services
Blasting Services Available
Testing & Quality Assurance
In-House Hardness Testing
Micro Scope – Image Analysis
- Microhardness Tester
- Portable Hardness Tester
Rockwell (RC, RB, RA)
- Superficial Hardness Tester (15N, 30N, 45N)
Brinell (HBW)
- Vickers Hardness Tester 5 To 50 Kg
Grain Size Analysis
Microstructure & Macrostructure Analysis
24-Hour Hardness
External Laboratory Testing Services
Tensile Testing (Room & Elevated Temperature)
Impact Testing
Stress Rupture & Creep Testing
Proof Load Testing
Chemical Analysis
Liquid Nitriding Furnaces
2 Liquid Nitriding Furnaces
Capacity: Up to 500 Kgs.
Furnace Size: 700mm” Diameter × 1500mm” Height
Liquid nitriding provides excellent surface hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength with controlled case depth and minimal distortion.
Sub - Zero Treatment Facility
Capacity: Up to 500 Kgs
Chamber Size: 3” W × 6” H × 4” Ft
Temperature Capability: Down to –150°F
Cryogenic treatment improves wear resistance, dimensional stability, and component life.
Vacuum Heat Treatment Processes
Tool Steel Heat Treatment
Stainless Steel Heat Treatment
Vacuum Age Hardening
Vacuum Full Annealing
Vacuum Normalizing
Vacuum Solution Annealing
Vacuum Tempering

Industries We Serve
Automotive
Aerospace
Tool & Die
Defense
Heavy Engineering
Foundries
Forging Units
Machine Components
